JDBC ARCHITECTURE
Unit Structure
14.1 Introduction to JDBC14.2 Java and JDBC
14.3 JDBC VS ODBC
14.4 JDBC DRIVER MODEL
14.5 JDBC Driver Types
14.6 Two-tier Architecture for Data Access
14.7 Three-tier Architecture for Data Access
14.8 SQL CONFORMANCE
14.9 Types of Driver Managers
14.1 Introduction to JDBC
JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. It is set of Java API‘s(application programming interface) used for executing SQL statements. This API consists of a set of classes and interfaces to enable programmers to write pure Java Database applications.JDBC is a software layer that allows developers to write real client –server projects in Java. JDBC does not concern itself with specific DBMS functions. JDBC API defines how an application opens a connection, communicates with a database, executes SQL statements, and retrieves query result. Following fig. will illustrate the role of JDBC. JDBC is based on the X/OPEN call level interface (CLI) for SQL.
Call Level Interface is a library of function calls that supports SQL statements. CLI requires neither host variables nor other embedded SQL concepts that would make it less flexible from a programmer‘s perspective. It is still possible, however, to maintain and use specific functions of a database management system when accessing the database through a CLI.
JDBC was designed to be very compact, simple interface focusing on the execution of raw SQL statements and retrieving the results. The goal of creating JDBC is to create an interface that keeps simple tasks, while ensuring the more difficult and uncommon tasks are at least made possible.
The following are the characteristics of JDBC.
- It is a call-level SQL interface for java
- It does not restrict the type of queries passed to an underlying DBMS driver
- JDBC mechanism are simple to understand and use
- It provides a java interface that stays consistent with the rest of the Java system
- JDBC may be implemented on top of common SQL level APIs.
Microsoft ODBC API offers connectivity to almost all databases on all platforms and is the most widely used programming interface for accessing relational database. But ODBC cannot be directly used with java programs due to various reasons enumerated in the JDBC vs. ODBC section. Hence the need for JDBC came into existence.
It is possible to access various relational databases like Sybase, Oracle, Informix, Ingers, using JDBC API. Using JDBC, we can write individual programs to connect to individual database or one program that take care of connecting to the respective database.
14.2 Java and JDBC
The combination of java with JDBC is very useful because it lets the programmer run his/her program on different platforms, Java programs are secure, robust, automatically downloaded from the network and java is a good language to create database applications. JDBC API enables Java applications to interact with different types of database. It is possible to publish vital information from a remote database on a web page using a java applet. With increasing inclination of programmers towards Java, knowledge about JDBC is essential.Some of the advantages of using Java with JDBC are as follows:
- Easy and economical
- Continued usage of already installed databases
- Development time is short
- Installation and version control simplified
How does JDBC work
JDBC defines a set of API objects and methods to interact with the underlying database. A Java program first opens a connection to the database, makes a statement object, passes SQL statements to the underlying database management system (DBMS) through the statement object and retrieve the results as well as information about the result set.
There are two types of interfaces – low –level interface and high-level interface. While high level interfaces are user-friendly, low-level interfaces are not. JDBC is a low-level API interface, ie. it used to invoke or call SQL commands directly. The required SQL statements are passed as strings to Java methods.
Some of the current trend that are being developed to add more features to JDBC are embedded SQL for java and direct mapping of relational database to java classes.
Embedded SQL enables mixing of java into SQL statements. These statements are translated into JDBC calls using SQL Processor. In this type of direct mapping of relational database tables to java, each row of the table becomes an instance of the class and each column value corresponds to an attribute of that instance. Mapping is being provided that makes rows of multiple tables to form a java class.
14.3 JDBC VS ODBC
The most widely used interface to access relational database today is Microsoft‘s ODBC API. ODBC performs similar tasks as that of JDC(Java Development Connection) and yet JDBC is preferred due to the following reasons :- ODBC cannot be directly used with Java because it uses a C interface. Calls from Java to native C code have a number of drawbacks in the security, implementation, robustness and automatic portability of applications.
- ODBC makes use of pointers which have been totally removed from Java
- ODBC mixes simple and advanced features together and has complex options for simple queries. But JDBC is designed to keep things simple while allowing advanced capabilities when required.
- JDBC API is a natural Java Interface and is built on ODBC. JDBC retains some of the basic features of ODBC like X/Open SQL Call Level Interface.
- JDBC is to Java programs and ODBC is to programs written in languages other than Java.
- ODBC is used between applications and JDBC is used by Java programmers to connect to databases.
Details about JDBC
The JDBC API is in the package java.sql it consists of 8 interfaces, 6 classes and 3 exceptions in JDK1.1.
Interfaces:
- CallableStatement
- Connection
- DatabaseMetaData Driver
- PreparedStatement
- ResultSet
- ResultSetMetaData
- Statement
Classes:
- Date
- DriverManager
- DriverPropertyInfo
- Time
- Timestamp
- Types
Exceptions:
- DataTruncation
- SQLException
- SQLWarning
14.4 JDBC DRIVER MODEL
14.5 JDBC Driver Types
There are 4 types of JDBC drivers. Commonest and most efficient of which are type 4 drivers. Here is the description of each of them:- JDBC Type 1 Driver - They are JDBC-ODBC Bridge drivers ie. Translate JDBC into ODBC and use Windows ODBC built in drivers. They delegate the work of data access to ODBC API. They are the slowest of all. SUN provides a JDBC/ODBC driver implementation.
- JDBC Type 2 Driver - They mainly use native API for data access ie. Converts JDBC to data base vendors native SQL calls and provide Java wrapper classes to be able to be invoked using JDBC drivers like Type 1 drivers; requires installation of binaries on each client.
- JDBC Type 3 Driver - Translates JDBC to a DBMS independent network protocol. They are written in 100% Java and use vendor independent Net-protocol to access a vendor independent remote listener. This listener in turn maps the vendor independent calls to vender dependent ones. This extra step adds complexity and decreases the data access efficiency.
- JDBC Type 4 Driver - They are also written in 100% Java and are the most efficient among all driver types. It compiles into the application, applet or servlet; doesn‘t require anything to be installed on client machine, except JVM. It also converts JDBC directly to native API used by the RDBMS.
The JDBC API supports both two-tier and three-tier processing models for database access.
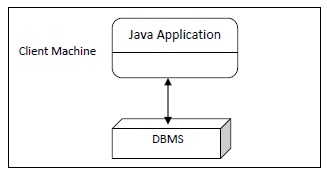
14.6 Two-tier Architecture for Data Access
- In the two-tier model, a Java application talks directly to the data source. This requires a JDBC driver that can communicate with the particular data source being accessed. A user's commands are delivered to the database or other data source, and the results of those statements are sent back to the user. The data source may be located on another machine to which the user is connected via a network. This is referred to as a client/server configuration, with the user's machine as the client, and the machine housing the data source as the server. The network can be an intranet, which, for example, connects employees within a corporation, or it can be the Internet.
- In the three-tier model, commands are sent to a "middle tier" of services, which then sends the commands to the data source. The data source processes the commands and sends the results back to the middle tier, which then sends them to the user. MIS directors find the three-tier model very attractive because the middle tier makes it possible to maintain control over access and the kinds of updates that can be made to corporate data. Another advantage is that it simplifies the deployment of applications. Finally, in many cases, the three-tier architecture can provide performance advantages.
14.7 Three-tier Architecture for Data Access
- Until recently, the middle tier has often been written in languages such as C or C++, which offer fast performance. However, with the introduction of optimizing compilers that translate Java byte code into efficient machine-specific code and technologies such as Enterprise JavaBeans™, the Java platform is fast becoming the standard platform for middle-tier development. This is a big plus, making it possible to take advantage of Java's robustness, multithreading, and security features.
- With enterprises increasingly using the Java programming language for writing server code, the JDBC API is being used more and more in the middle tier of a three-tier architecture. Some of the features that make JDBC a server technology are its support for connection pooling, distributed transactions, and disconnected row sets. The JDBC API is also what allows access to a data source from a Java middle tier.
14.8 SQL CONFORMANCE
Structured Query Language (SQL) is the standard language used to access relational databases, unfortunately, there are no standards set at present for it for ex, problems may arise due to the variations in different data types of different databases. JDBC defines a set of generic SWL types identifiers in the class Java.SQL.TypesWays of dealing with SQL conformance
JDBC deals with SQL conformance by performing the following :
- JDBC API allows any query string to be passed through to an underlying DBMS driver. But there are possibilities of getting an error on some DBMS.
- Provision of ODBC style escape closes.
- Provision of descriptive information about the DBMS using an interface, DatabaseMetaData.
The designation JDBC Compliant was created to set a standard level of JDBC functionality on which users can rely. Only the ANSI SQL 2 enty level supported drivers can make use of this designation. The conformance tests check for the existence of all classes and methods defined in the JDBC API and SQL entry level functionality.
14.9 Types of Driver Managers
JDBC contains three components: Application, Driver Manager, Driver. The user application invokes JDBC methods to send SQL statements to the database and retrieves results. JDBC driver manager is used to connect Java applications to the correct JDBC driver . JDBC driver test suite is used to ensure that the installed JDBC driver is JDBC Compliant. There are four different types of JDBC drivers as follows1.The JDBC-ODBC Bridge plus ODBC driver :
The JDBC-ODBC Bridge plus ODBC driver is a JavaSoft Bridge protocol that provides JDBC access via ODBC drivers. But as we have mentioned earlier, combining ODBC brings in a lot of drawbacks and limitations, since the ODBC driver has to be installed on each client machine, it is not advisable to choose this type of driver for large networks.2. Native-API partly-Java driver :
Native-API partly-Java driver converts JDBC calls into calls on the client API for Oracle, Sybase, Informix or other DBMS. But some binary code has to be loaded on all client like the bridge driver and hence is not suitable for large networks.
3.JDBC-Net pure Java driver:
JDBC-Net pure Java driver translates JDBC calls into DBMS independent net protocol. A server again translates this protocol to a DBMS protocol. The net server middleware connects its pure Java clients to many different databases. The type of protocol in this middleware depends on the vendor.
4.Native-protocol pure Java driver :
Native-protocol pure Java driver convert JDBC calls to network protocols used by the DBMSs directly. Requests from client machines are made directly to the DBMS server.
Drivers 3 and 4 are the most preferred ways to access databases from JDBC drivers.






No comments:
Post a Comment